
The Global Use of Medicine in 2019 and Outlook to 2023 / Forecasts and Areas to Watch
04 February 2019
About the Report
 The global outlook for medicine use and spending affects the prospects of life sciences companies, insurers and the health of populations around the world. This report includes the latest predictions for the global pharmaceutical market along with geographic, therapy area and channel perspectives. It assesses the impact of new drug launches, biosimilars, and growth in the use of specialty medicines. The report also highlights ten areas to watch over the next several years that impact the use of and cost of medicines including: prescription digital health tools, artificial intelligence and machine learning, Next-Generation Biotherapeutics and use of real-world evidence in clinical development.
The global outlook for medicine use and spending affects the prospects of life sciences companies, insurers and the health of populations around the world. This report includes the latest predictions for the global pharmaceutical market along with geographic, therapy area and channel perspectives. It assesses the impact of new drug launches, biosimilars, and growth in the use of specialty medicines. The report also highlights ten areas to watch over the next several years that impact the use of and cost of medicines including: prescription digital health tools, artificial intelligence and machine learning, Next-Generation Biotherapeutics and use of real-world evidence in clinical development.
Report Summary
The global pharmaceutical market will exceed $1.5 trillion by 2023 growing at a 3−6% compound annual growth rate over the next five years. The key drivers of growth will continue to be the United States and pharmerging markets with 4−7% and 5–8% compound annual growth, respectively. In the United States, overall spending growth is driven by a range of factors including new product uptake and brand pricing, while it is offset by patent expiries and generics. Medicine spending in Japan totaled $86 billion in 2018, however spending on medicines is expected to decline by -3 to 0% through 2023, largely because of exchange rates and the continued uptake of generics. In Europe, cost-containment measures and less growth from new products contribute to slower growth of 1−4%, compared to the 4.7% compound annual growth seen over the past five years. Pharmaceutical spending in China reached $137 billion in 2018 and is expected to reach $140−170 billion by 2023, but its growth is likely to slow to 3−6%.
New products and losses of exclusivity will continue to drive similar dynamics across developed markets, while product mix will continue to shift to specialty and orphan products. An average of 54 new active substance (NAS) launches per year are expected over the next five years and two-thirds of launches will be specialty products, lifting specialty share of spending to near 50% by 2023 in most developed markets. At the same time, the impact of losses of exclusivity in developed markets is expected to be $121 billion between 2019 and 2023, with 80% of this impact, or $95 billion, in the United States. By 2023, biosimilar competition in the biologics market will be nearly three-times larger than it is today. This will result in approximately $160 billion in lower spending over the next five years than it would have if biosimilars did not enter the market.
In addition to these market forecasts, there are several areas to watch. These include:
- Expanding use of Next-Generation Biotherapeutics (e.g. cell-based therapies, gene therapies and regenerative medicines
- Emergence of prescription digital therapeutics
- Trends in global health
- Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Expanding use of real-world evidence in trial design
- An increase in patient advocacy roles within pharma
- Enactment of U.S. pricing policy reforms
- Growing influence of emerging biopharma companies
- The trajectory of the opioid epidemic in the United States
- Use of technology and innovation to drive efficiencies in large pharma
Key Findings
Global spending on medicines reached $1.2 trillion in 2018 and is set to and is set to exceed $1.5 trillion by 2023
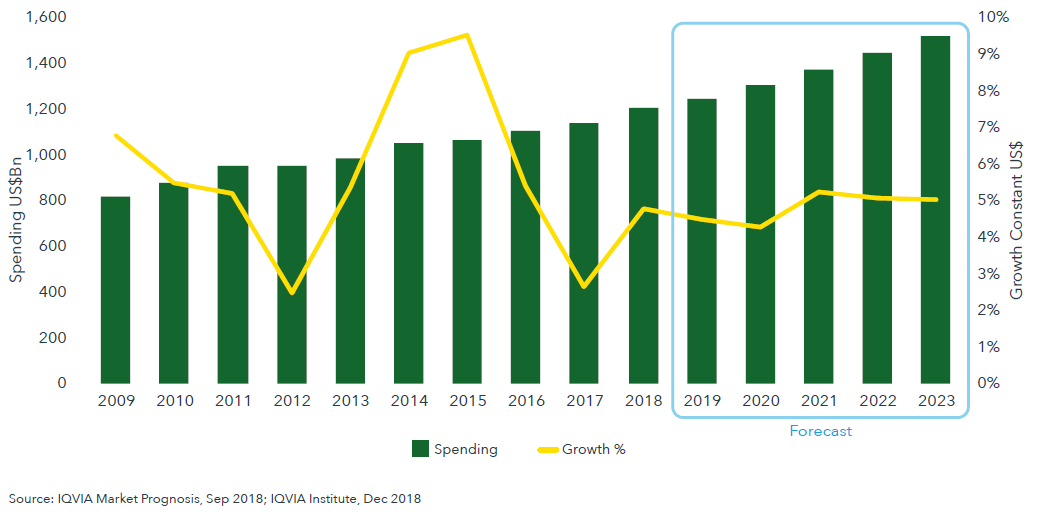
- Global growth of medicine spending through 2023 will be influenced by the U.S. market. It will be driven by launches of new products and offset by losses of exclusivity of branded products and the growth of biosimilars.
- Spending on medicines in the U.S. is expected to reach over $600 billion on an invoice basis in 2023.
- Global growth will be driven to a lesser extent by expanded access and use of medicines in pharmerging markets, with China’s growth leading it to approach the combined spending level of the five major European markets by 2023.
- Other developed markets are showing pockets of growth. Spending in Japan totaled $86 billion in 2018, however, over the next five years, spending is expected to decline from -3 to 0% on a constant dollar basis due in large part to exchange rate dynamics and continued uptake of generics.
In the United States, the median list price for oncology and orphan drugs could potentially reach above $200,000 per year by 2023
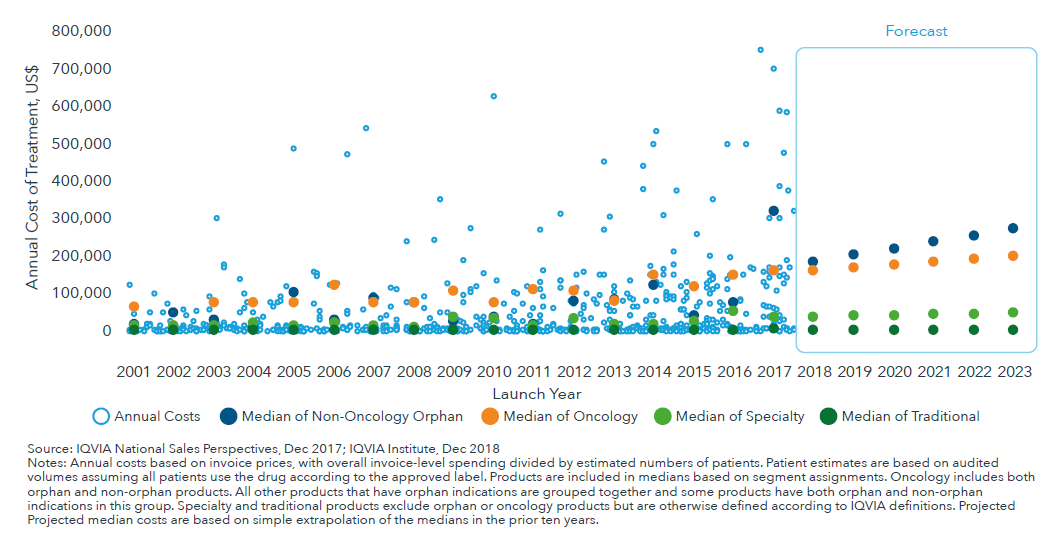
- While the median annual cost for new medicines in specialty, orphan and oncology are rising traditional drug costs are not rising as rapidly.
- Higher prices are in part the result of new drugs shifting to treat smaller populations, with 30% and 45% of expected novel active substances in the next five years being oncology and orphan drugs, respectively.
In the past two years, a range of companies made commitments to reduce list price increases for branded medicines, which are now below 6% per year on average
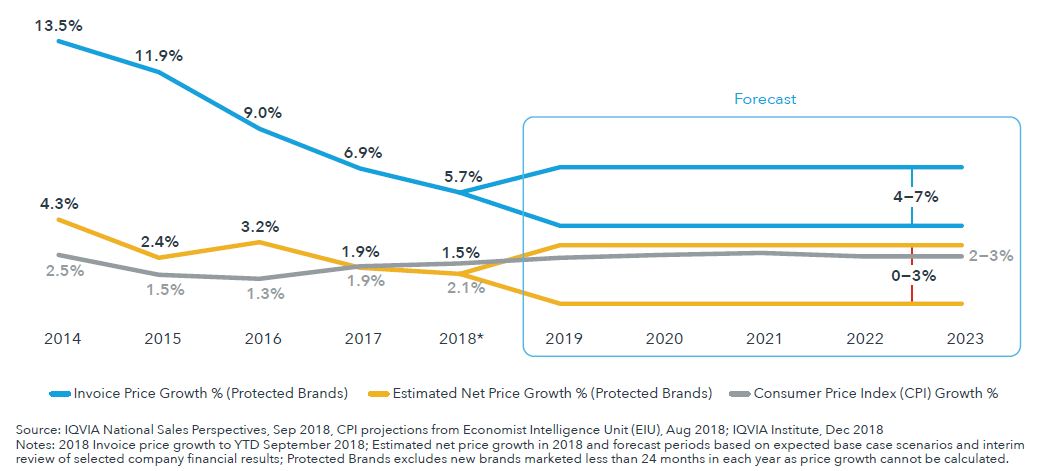
- U.S. List price increases are expected to remain in the range of 4–7 percent through 2023.
- The net prices manufacturers receive for drugs increased at an estimated 1.5% in 2018 and are expected to rise at 0–3% over the next five years.
- Net price growth was below inflation in the wider economy in 2018; an occurrence expected to continue for the next five years.
Biosimilar dynamics will be driven in the near-term by molecules that are already facing competition and may see new competitors, while key introductions of new biosimilars in 2023 will impact in the longer-term
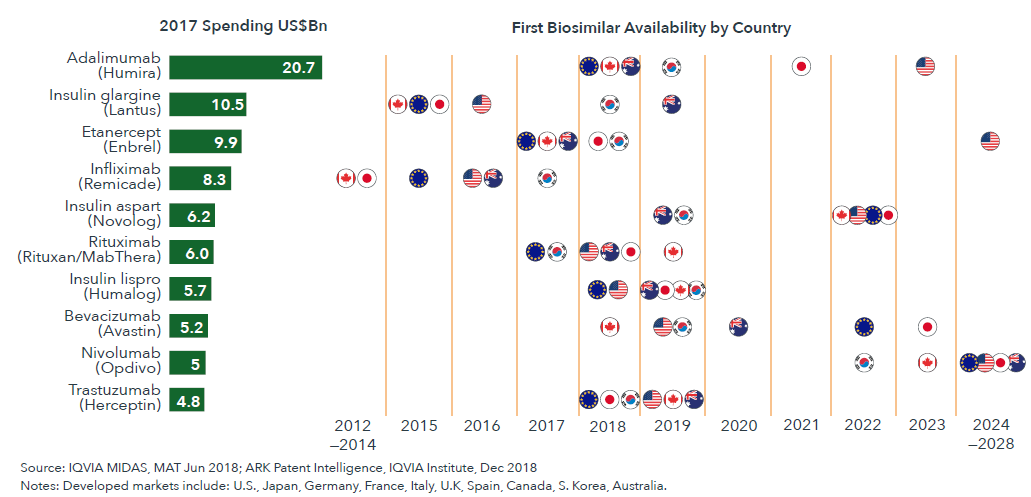
- Across developed markets, there will be fewer losses of exclusivity and associated market entry events by biosimilars after 2019 through 2023.
- By 2023, the part of the biologic market with competition from biosimilars will be nearly three-times larger than it is today, and the presence of that competition will result in nearly $160 billion in lower spending over the next five years in the U.S.
- The biggest single event in the biosimilars market in the next five years will be the introduction of adalimumab (Humira) biosimilars in the United States in 2023.
There are additionally 10 areas to watch in the market including scenarios for continued decline in prescription opioids in the United States
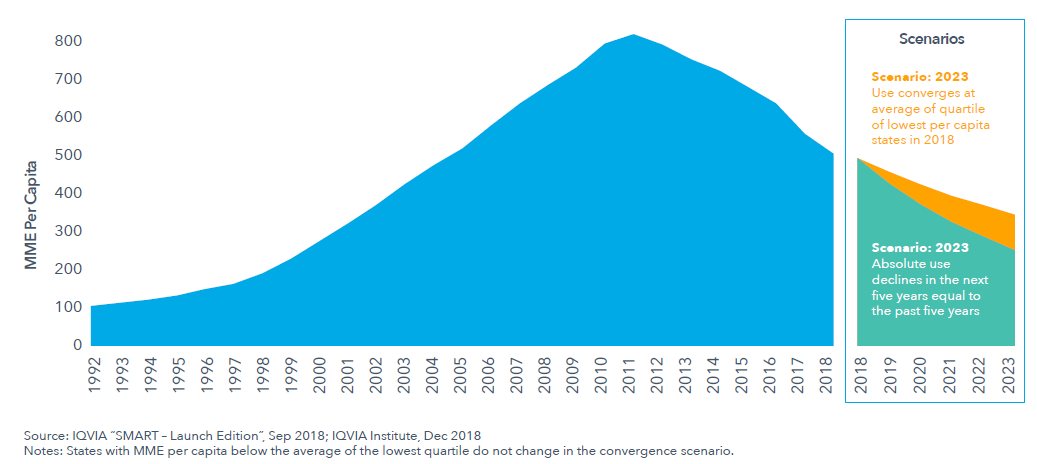
- After seven straight years of declining prescription opioid use in the United States, the current rate of decline could continue or begin to decline more slowly.
- One projected scenario describes five more years following rates of decline from 2013−2018. It reflects continued implementation and impact of policies, laws and practice guidelines introduced over the past two years at the state and federal levels and the likely implementation of new policies.
- The other projected scenario describes higher-use states adopting policies that enable them to converge at a lower level of prescription opioid use, but lower-use states will be unable to continue their dramatic reductions in use.
Our news
-
14 March 2024
-
26 February 2024
-
NovaMedica team wishes you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year!
26 December 2023
Media Center
-
Russian drug for the treatment of viral hepatitis will be exempt from duty in Mongolia
24 April 2024
-
PM Mishustin: “We need to increase the production of vital and essential drugs in Russia”
24 April 2024
-
The Future of Pharmacy: How Advancements in Technology Are Transforming the Field
23 April 2024
-
Analysis Forecasts Up to 16.5% of Population Will Have Chronic Kidney Disease by 2032
23 April 2024